- Hash Table is a data structure which stores data in an associative manner. In a hash table, data is stored in an array format, where each data value has its own unique index value. Access of data becomes very fast if we know the index of the desired data.
- Thus, it becomes a data structure in which insertion and search operations are very fast irrespective of the size of the data. Hash Table uses an array as a storage medium and uses hash technique to generate an index where an element is to be inserted or is to be located from.
Hash Table for Customer Details
- If we want to store the customer details and want to search them in well manner, we can use a hash table and linear hashing.
- We take customer details like customer name, customer id, and customer phone.
- We create a Hash table for customers then insert the data based on the hash key.
- During a searching, we can search them based on the hash key only.
- If two keys point to same location, then we use Linear probe resolution method for resolving collision.

Linear Probe Resolution Method :
- Linear probing is a scheme in computer programming for resolving collisions in hash tables, data structures for maintaining a collection of key–value pairs and looking up the value associated with a given key.
- Along with quadratic probing and double hashing, linear probing is a form of open addressing. In these schemes, each cell of a hash table stores a single key–value pair. When the hash function causes a collision by mapping a new key to a cell of the hash table that is already occupied by another key, linear probing searches the table for the closest following free location and inserts the new key there.
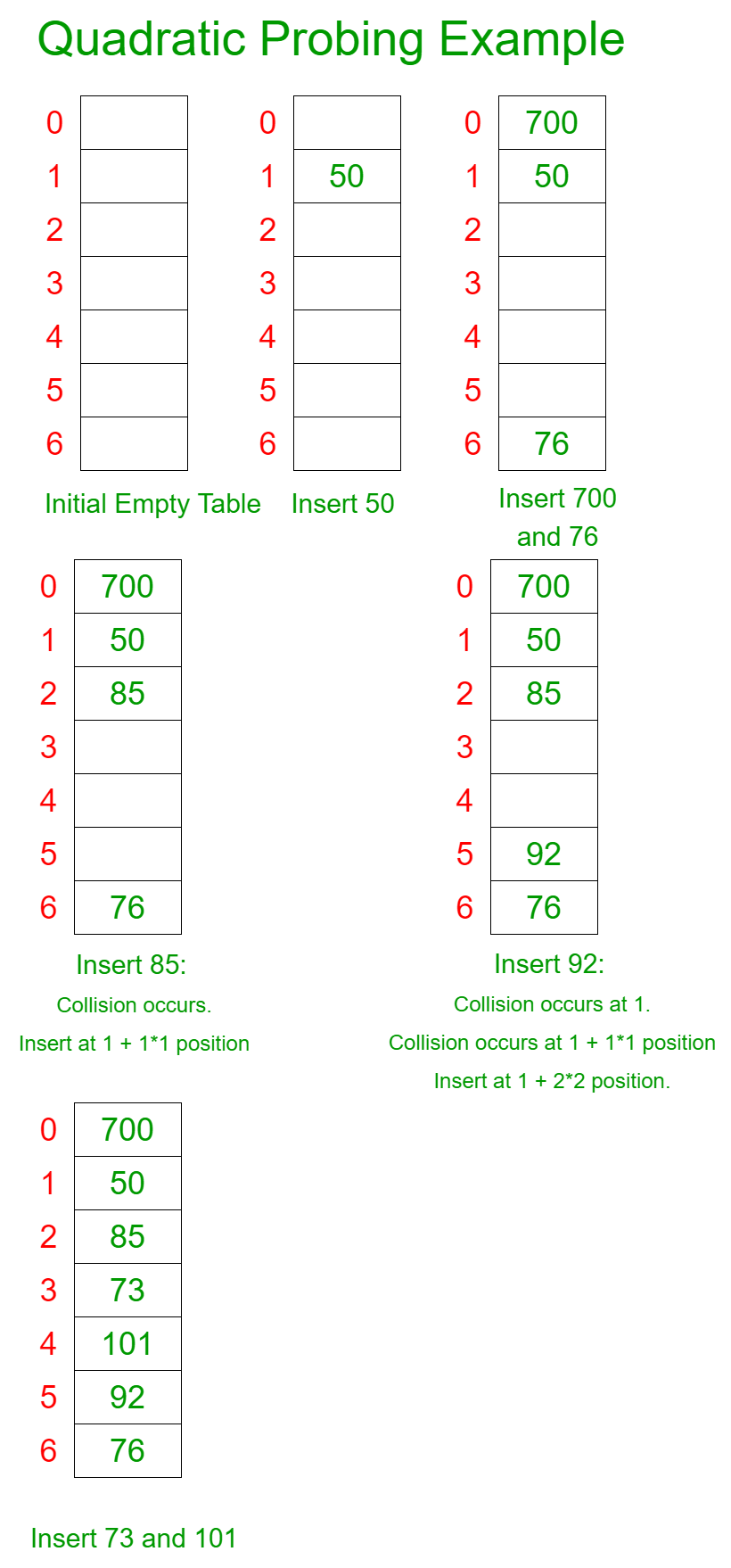
Quadratic Probing
Quadratic probing is an open-addressing scheme where we look for the i2‘th slot in the i’th iteration if the given hash value x collides in the hash table.
- How Quadratic Probing is done?
Features
- The Inserting and Searching in the hash table is very easy compared to other data structures.
- There is very less chance of collision especially when we use linear probe.
Pseudo code
- Generate a hash key for a entry
- If the place pointed by hash key is empty, Insert a data at that position
- Else, Loop until we get a empty position
- If, there is no empty location print hash table full
- Generate a hash key for given key
- If the location pointed by hash key is empty, return -1
- If that location contains desired key, return position
- else, loop until we get desired key
- If the key is not found return -1
- Loop(until last position)
- If the position contains data, print data
- else, print no hash entry
- end loop
Time complexity
- `Searching : O(1)
- Inserting : O(1)`
Advantages :
- Hash table is very useful when we have huge amount of data
- Searching a data in a table is very fast.
Disadvantages :
- Only limited entries in a Hash table. Big data should be manage otherwise.
- If collision occurs, we must take care of it.
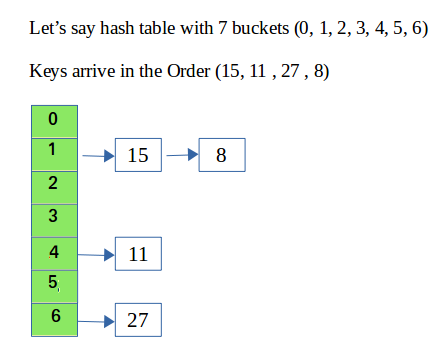
Chaining
In hashing there is a hash function that maps keys to some values. But these hashing function may lead to collision that is two or more keys are mapped to same value. Chain hashing avoids collision. The idea is to make each cell of hash table point to a linked list of records that have same hash function value.
Let’s create a hash function, such that our hash table has ‘N’ number of buckets.
To insert a node into the hash table, we need to find the hash index for the given key. And it could be calculated using the hash function.
Example: hash Index = key % noOfBucketsInsert: Move to the bucket corresponds to the above calculated hash index and insert the new node at the end of the list. Delete: To delete a node from hash table, calculate the hash index for the key, move to the bucket corresponds to the calculated hash index, search the list in the current bucket to find and remove the node with the given key (if found).

Time Complexity:
- Search : O(1+(n/m))
- Delete : O(1+(n/m))where n = Total elements in hash table m = Size of hash table
- Here n/m is the Load Factor.
- Load Factor (∝) must be as small as possible.
- If load factor increases, then possibility of collision increases.
- Load factor is trade of space and time .
- Assume , uniform distribution of keys ,
- Expected chain length : O(∝)
- Expected time to search : O(1 + ∝)
- Expected time to insert/ delete : O(1 + ∝)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), since no extra space has been taken.
Chaining in Hashing with Linked List (Extra)
Chaining in hashing is a technique used to resolve collisions in hash tables. It involves creating a linked list for each bucket in the hash table, and inserting elements into the linked list if a collision occurs. This technique can be used to store and access data efficiently, as it reduces the number of collisions and improves the performance of hash tables.
Advantages
Chaining in hashing has several advantages, including:
- Easy to implement: Chaining in hashing is easy to implement, as it only requires the use of linked lists.
- Improved performance: Chaining in hashing reduces the number of collisions, which improves the performance of hash tables and makes data access more efficient.
- Flexible: Chaining in hashing is flexible, as it can be used with any type of data structure.
Disadvantages
Chaining in hashing also has some disadvantages, including:
- Increased memory usage: Chaining in hashing requires additional memory to store the linked lists.
- Slower search time: Chaining in hashing can slow down the search time if the linked list is long.
Conclusion (when to use where)
In general, you should use probing when the number of collisions is expected to be low and when the keys are evenly distributed throughout the hash table. You should use separate chaining when the number of collisions is expected to be high or when the keys are not evenly distributed. It is also worth noting that other collision resolution methods, such as open addressing, exist and may be more suitable for certain applications.
Applications Of Hash Tables




